Aortic Valve Insufficiency: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "Quantification Aortic valve insufficiency Quantification Aortic valve insufficiency Slight Moderate Severe Jet / LVOT <25 % 25-65 % > 65% PHT > 500m / s 500 - 300m / s < 30...") |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Quantification Aortic valve insufficiency | ==Quantification Aortic valve insufficiency== | ||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" width="700px" | |||
|- | |||
Slight Moderate Severe | ! | ||
Jet / LVOT <25 % 25-65 % > 65% | !Slight | ||
PHT > 500m / s 500 - 300m / s < 300m / s | !Moderate | ||
Vena contracta < 3mm - 6mm | !Severe | ||
|- | |||
|align="center"|Jet/LVOT | |||
|align="center"|<25% | |||
|align="center"|25-65% | |||
|align="center"|>65% | |||
|- | |||
|align="center"|PHT | |||
|align="center"|>500m/s | |||
|align="center"|500-300m/s | |||
|align="center"|<300m/s | |||
|- | |||
|align="center"|Vena contracta | |||
|align="center"|<3mm | |||
|align="center"|3-6mm | |||
|align="center"|>6mm | |||
|} | |||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | |||
|- | |||
|[[Image:AoIVC.jpg|350px]] | |||
|[[Image:AoIPHT.jpg|350px]] | |||
|- | |||
!Wide vena contracta <cite>1</cite> | |||
!PHT moderate Aol <cite>1</cite> | |||
|} | |||
==Jet width ratio relative LVOT== | |||
Currently the most widely used and best documented measurement to assess the severity of aortic insufficiency, however it has limitations in poor parasternal (Plax) windows and eccentric jets. | |||
PLAX: Jet width/width left ventricular outflow-tract x 100% | |||
Pulsed - wave Doppler of flow in descending aortic | ==Pressure half-time (PHT)== | ||
Retrograde flow in Ao - descending , supra sternal immediately after subclavian artery measured by pulsed- wave Doppler . | The pressure half-time depends on both the volume as regurgitation of the diastolic function of the left ventricle (compliance). However, in severe aortic valve insufficiency of the left ventricle is more likely to become "full" so that the pressure half-time will be short, this may result in diastolic mitral regurgitation to occur. Also this will make the pressure half-time to shorten. Thus completing the diastolic function of the left ventricle with a poorly tolerated aortic valve insufficiency. | ||
If end diastolic flow velocity : | |||
< 18 cm / s | ==Vena contracta== | ||
> 18 cm / s indicates | The VC appears to correlate with the effective surface regurgitation (ERO) very well. In addition, the VC is found to be of the afterload or diastolic function of the left ventricle. Independently this seems to be the severity of aortic valve insufficiency of a very good size. | ||
In severe Aoi | |||
TVI backflow signal > | A VC diameter> 6mm appears to have a serious, very good sensitivity and specificity Aoi. | ||
A VC <5mm suggests a non-serious Aoi. | |||
==Pulsed - wave Doppler of flow in descending aortic== | |||
Retrograde flow in Ao-descending, supra sternal immediately after subclavian artery measured by pulsed-wave Doppler. | |||
If end diastolic flow velocity: | |||
<18 cm/s does not indicate hemodynamically significant AOI (grade I and II) | |||
>18 cm/s indicates hemodynamically significant Aol (grade III and IV) | |||
In severe then Aoi initially> 0.6 m/s | |||
TVI backflow signal> 15cm | |||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | |||
|- | |||
|bgcolor="FFFFFF" colspan="2" align="center"|[[File:600px-Aodescflow.svg|600px]] | |||
|- | |||
!width="250px"|Normal descending flow | |||
!Holo Diastolic flow reversal in descending aorta | |||
|} | |||
==References== | |||
<biblio> | |||
#1 pmid=20375260 | |||
</biblio> | |||
Latest revision as of 08:42, 28 March 2014
Quantification Aortic valve insufficiency
| Slight | Moderate | Severe | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jet/LVOT | <25% | 25-65% | >65% |
| PHT | >500m/s | 500-300m/s | <300m/s |
| Vena contracta | <3mm | 3-6mm | >6mm |
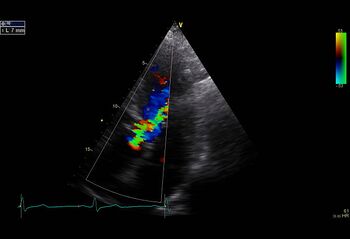
|
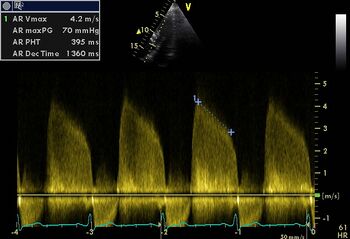
|
| Wide vena contracta [1] | PHT moderate Aol [1] |
|---|
Jet width ratio relative LVOT
Currently the most widely used and best documented measurement to assess the severity of aortic insufficiency, however it has limitations in poor parasternal (Plax) windows and eccentric jets.
PLAX: Jet width/width left ventricular outflow-tract x 100%
Pressure half-time (PHT)
The pressure half-time depends on both the volume as regurgitation of the diastolic function of the left ventricle (compliance). However, in severe aortic valve insufficiency of the left ventricle is more likely to become "full" so that the pressure half-time will be short, this may result in diastolic mitral regurgitation to occur. Also this will make the pressure half-time to shorten. Thus completing the diastolic function of the left ventricle with a poorly tolerated aortic valve insufficiency.
Vena contracta
The VC appears to correlate with the effective surface regurgitation (ERO) very well. In addition, the VC is found to be of the afterload or diastolic function of the left ventricle. Independently this seems to be the severity of aortic valve insufficiency of a very good size.
A VC diameter> 6mm appears to have a serious, very good sensitivity and specificity Aoi.
A VC <5mm suggests a non-serious Aoi.
Pulsed - wave Doppler of flow in descending aortic
Retrograde flow in Ao-descending, supra sternal immediately after subclavian artery measured by pulsed-wave Doppler.
If end diastolic flow velocity:
<18 cm/s does not indicate hemodynamically significant AOI (grade I and II)
>18 cm/s indicates hemodynamically significant Aol (grade III and IV)
In severe then Aoi initially> 0.6 m/s
TVI backflow signal> 15cm
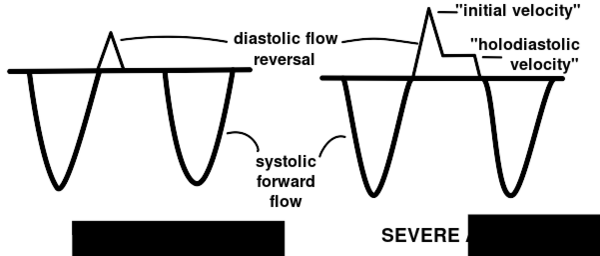
| |
| Normal descending flow | Holo Diastolic flow reversal in descending aorta |
|---|---|
References
- Lancellotti P, Tribouilloy C, Hagendorff A, Moura L, Popescu BA, Agricola E, Monin JL, Pierard LA, Badano L, Zamorano JL, and European Association of Echocardiography. European Association of Echocardiography recommendations for the assessment of valvular regurgitation. Part 1: aortic and pulmonary regurgitation (native valve disease). Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010 Apr;11(3):223-44. DOI:10.1093/ejechocard/jeq030 |