Cause: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "Cardiac Arrest Ultra Sound Exam ( CAUSE ) Cardiac arrest is a condition that often occurs in the Emergency Department , Intensive Care Unit and the surgical wards . The use of...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Cardiac Arrest Ultra Sound Exam ( CAUSE ) | Cardiac Arrest Ultra Sound Exam (CAUSE) | ||
Cardiac arrest is a condition that often occurs in the Emergency Department , Intensive Care Unit and the surgical wards . | Cardiac arrest is a condition that often occurs in the Emergency Department, Intensive Care Unit and the surgical wards. | ||
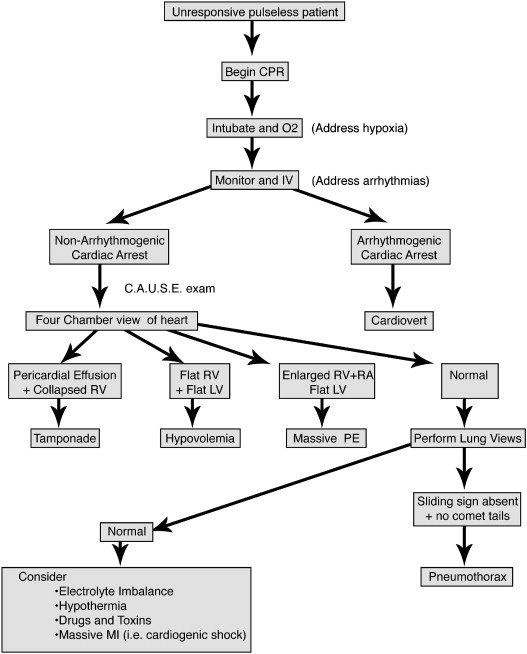
The use of ultrasound in resuscitation plays an important role in order to differentiate between the different causes of cardiac arrest, which are not a direct consequence of a primary ventricular arrhythmia. The most common and reversible causes of cardiac arrest include: severe hypovolemia , pneumothorax , cardiac tamponade , and massive pulmonary embolism . Identifying the underlying cause of cardiac arrest is one of the biggest challenges . This is the CAUSE protocol developed . | The use of ultrasound in resuscitation plays an important role in order to differentiate between the different causes of cardiac arrest, which are not a direct consequence of a primary ventricular arrhythmia. The most common and reversible causes of cardiac arrest include: severe hypovolemia, pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, and massive pulmonary embolism. Identifying the underlying cause of cardiac arrest is one of the biggest challenges. This is the CAUSE protocol developed. | ||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | |||
|[[Image:Cause flowchart.jpg|600px]] | |||
|- | |||
!Flowchart of the protocol CAUSE<cite>1</cite> | |||
|} | |||
==Echocardiographic findings== | |||
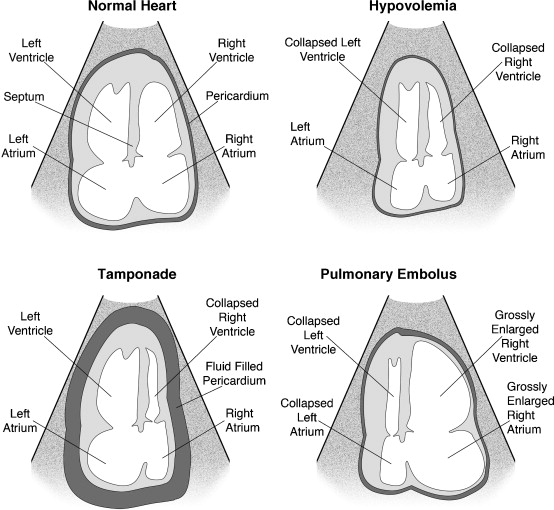
Echocardiography is the only mode with the possibility to in real-time during a cardiac arrest without interfering with the CPR. Moreover, there may be direct when resuscitating a diagnosis and are thus time savings are made between the judgment and appropriate treatment. Below are several clinical findings that differentiate between cardiac tamponade, pneumothorax, pulmonary embolism, and severe hypovolemia secondary to abdominal aortic aneurysm. | |||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | |||
!Subcostale views | |||
!Tamponade | |||
!Hypovolemie | |||
!Longembolie | |||
!Pneumothorax | |||
|- | |||
!VCI | |||
|align="center"|>20mm | |||
|align="center"|<5mm | |||
|align="center"|>20mm | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
!Pericard | |||
|Many pericardial | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|"Sliding sign" | |||
|- | |||
!RV | |||
|Collapsed |Collapsed | |||
|Dilated | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
!LV | |||
| | |||
|Flattened septum | |||
|Flattened septum | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
Echocardiographic findings | {| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | ||
Echocardiography is the only mode with the possibility to in real-time during a cardiac arrest without interfering with the CPR. Moreover, there may be direct when resuscitating a diagnosis and are thus time savings are made between the judgment and appropriate treatment . Below are several clinical findings that differentiate between cardiac tamponade , pneumothorax , pulmonary embolism , and severe hypovolemia secondary to abdominal aortic aneurysm . | |[[Image:Cause flowchart.jpg|600px]] | ||
Subcostale views Tamponade | |- | ||
VCI > 20mm < 5mm > 20mm - | !Ultrasound findings in a AP4Ch view. Note: images are mirrored display.<cite>1</cite>Cardiac Arrest Ultra Sound Exam (CAUSE) | ||
Many pericardial | Cardiac arrest is a condition that often occurs in the Emergency Department, Intensive Care Unit and the surgical wards. | ||
RV | The use of ultrasound in resuscitation plays an important role in order to differentiate between the different causes of cardiac arrest, which are not a direct consequence of a primary ventricular arrhythmia. The most common and reversible causes of cardiac arrest include: severe hypovolemia, pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, and massive pulmonary embolism. Identifying the underlying cause of cardiac arrest is one of the biggest challenges. This is the CAUSE protocol developed. | ||
LV | |||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | |||
|[[Image:Cause flowchart.jpg|600px]] | |||
|- | |||
!Flowchart of the protocol CAUSE<cite>1</cite> | |||
|} | |||
==Echocardiographic findings== | |||
Echocardiography is the only mode with the possibility to in real-time during a cardiac arrest without interfering with the CPR. Moreover, there may be direct when resuscitating a diagnosis and are thus time savings are made between the judgment and appropriate treatment. Below are several clinical findings that differentiate between cardiac tamponade, pneumothorax, pulmonary embolism, and severe hypovolemia secondary to abdominal aortic aneurysm. | |||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | |||
!Subcostale views | |||
!Tamponade | |||
!Hypovolemie | |||
!Longembolie | |||
!Pneumothorax | |||
|- | |||
!VCI | |||
|align="center"|>20mm | |||
|align="center"|<5mm | |||
|align="center"|>20mm | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
!Pericard | |||
|Many pericardial | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|"Sliding sign" | |||
|- | |||
!RV | |||
|Collapsed |Collapsed | |||
|Dilated | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
!LV | |||
| | |||
|Flattened septum | |||
|Flattened septum | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" | |||
Ultrasound findings in a AP4Ch view . Note: images are mirrored display. | |[[Image:CAUSE02.jpg|600px]] | ||
|- | |||
!Ultrasound findings in a AP4Ch view. Note: images are mirrored display.<cite>1</cite> | |||
|} | |||
Tamponade Pulmonary Embolism | |||
Source: Resuscitation. 2008 Feb ; 76 (2) :198-206. | |||
==References== | |||
<biblio> | |||
#1 pmid=17822831 | |||
</biblio> | |||
|} | |||
Tamponade Pulmonary Embolism | Tamponade Pulmonary Embolism | ||
Source: Resuscitation. 2008 Feb ; 76 (2) :198-206 . | Source: Resuscitation. 2008 Feb ; 76 (2) :198-206. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
#1 pmid= | #1 pmid=17822831 | ||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
Revision as of 05:09, 2 February 2014
Cardiac Arrest Ultra Sound Exam (CAUSE) Cardiac arrest is a condition that often occurs in the Emergency Department, Intensive Care Unit and the surgical wards. The use of ultrasound in resuscitation plays an important role in order to differentiate between the different causes of cardiac arrest, which are not a direct consequence of a primary ventricular arrhythmia. The most common and reversible causes of cardiac arrest include: severe hypovolemia, pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, and massive pulmonary embolism. Identifying the underlying cause of cardiac arrest is one of the biggest challenges. This is the CAUSE protocol developed.
|
| Flowchart of the protocol CAUSE[1] |
|---|
Echocardiographic findings
Echocardiography is the only mode with the possibility to in real-time during a cardiac arrest without interfering with the CPR. Moreover, there may be direct when resuscitating a diagnosis and are thus time savings are made between the judgment and appropriate treatment. Below are several clinical findings that differentiate between cardiac tamponade, pneumothorax, pulmonary embolism, and severe hypovolemia secondary to abdominal aortic aneurysm.
| Subcostale views | Tamponade | Hypovolemie | Longembolie | Pneumothorax |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCI | >20mm | <5mm | >20mm | |
| Pericard | Many pericardial | "Sliding sign" | ||
| RV | Collapsed | Dilated | ||
| LV | Flattened septum | Flattened septum |

| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ultrasound findings in a AP4Ch view. Note: images are mirrored display.[1]Cardiac Arrest Ultra Sound Exam (CAUSE)
Cardiac arrest is a condition that often occurs in the Emergency Department, Intensive Care Unit and the surgical wards. The use of ultrasound in resuscitation plays an important role in order to differentiate between the different causes of cardiac arrest, which are not a direct consequence of a primary ventricular arrhythmia. The most common and reversible causes of cardiac arrest include: severe hypovolemia, pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, and massive pulmonary embolism. Identifying the underlying cause of cardiac arrest is one of the biggest challenges. This is the CAUSE protocol developed.
Echocardiographic findingsEchocardiography is the only mode with the possibility to in real-time during a cardiac arrest without interfering with the CPR. Moreover, there may be direct when resuscitating a diagnosis and are thus time savings are made between the judgment and appropriate treatment. Below are several clinical findings that differentiate between cardiac tamponade, pneumothorax, pulmonary embolism, and severe hypovolemia secondary to abdominal aortic aneurysm.
Source: Resuscitation. 2008 Feb ; 76 (2) :198-206. References |
|---|
Tamponade Pulmonary Embolism
Source: Resuscitation. 2008 Feb ; 76 (2) :198-206.