Benign tumors
Usually, a cardiac tumor is benign in nature. A benign tumor has a good prognosis at thrombi. Vegetations and some tumors are the most at risk embolism.
| (Primary) Benign tumors
|
| Myxoma
|
- Most common primary cardiac tumor (50-75%).
- Location: 90% atrial (LA 75%), 7% ventricular.
- Size: 1 - 15cm (usually 5 - 6cm)
|
| Fibroma
|
- The second most common primary cardiac tumor.
- Location: Almost always ventricular (septal or apical).
- Size: ± 10cm.
|
| Papillary fibroelastoma
|
- Most common valve tumor.
- Location: whole heart, usually aortic valve (35%).
- Size: ± 1cm.
|
| Lipoma
|
- Usually, on the basis of the endocardium.
- Location: whole heart including valves and pericardium.
- Size: up to ± 10cm.
|
| Rhabdomyoma
|
- Most common benign cardiac tumor in children.
- Location: usually ventricular, no valve involvement.
- Size: 1mm - 9cm.
|
| Hemangioma
|
- Tumor blood, proliferation endothelial cells
- Location: whole heart
|
| Lambl's excrescences
|
- Valvular choir dd. fibroelastoma, thrombus, vegetation.
- Location: ventricular side of aortic valve.
- Size: ± 1cm
|
| Cysts
|
- Congenital unnatural body cavity delimited by epithelium.
- Location: usually in the right atrium (right cardiophrenic corner).
|
| Thrombi
|
- Clots of blood by slow blood flow.
- Location: Left atrial appendage in atrial fibrillation, akinetic myocardial infarction or cardiomyopathies, prosthetic valves or infectious valves, atrial septal ASD/PFO.
|
Malignant tumors
Primary malignant tumors are very rare. The most common malignant cardiac tumors are secondary tumors derived from primary diseases (see table below). 3% of all patients with cancer receive cardiac metastases through the four "pathways": direct infiltration, haematogenically (through blood), lymph vessels (VCI, pulmonary veins). Malignant tumors have a poor prognosis: In malignant tumors the major risk is of the malignancy itself.
| Primary malignant tumors
|
| Angiosarcoma
|
- Most common primary malignant cardiac tumor
- Location: 90% right atrium
|
| Rhabdomyosarcoma
|
- Second most common primary malignant cardiac tumor, often in children than adults
- Location: whole heart
|
| Mesothelioma
|
- Cover visceral and parietal pericardium, no growth in endocardium.
|
| Secondary malignant tumors
|
| Metastases
|
- Melanoma
- Lung Cancer
- Breast cancer
- Sarcoma
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Leukemia
- Lymphoma
- Oesophagus cancer
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Thyroid cancer
|
Overview of the locations of the most common cardiac tumors
| Location
|
Tumor
|
| left atrium
|
- Myxoma
- Thrombus
- Papillary fibroelastoma
- Sarcoma
|
| Eight atrium
|
- Myxoma
- Angiosarcoma
- Lymphoma
- Thrombus
- Papillary fibroelastoma
|
| Left ventricular
|
- Fibroma
- Rhabdomyoma
- Thrombus
- Papillary fibroelastoma
|
| Right ventricle
|
- Fibroma
- Rhabdomyoma
- Angiosarcoma
- Lymphoma
- Thrombus
- Papillary fibroelastoma
|
Examples1
| Video
|
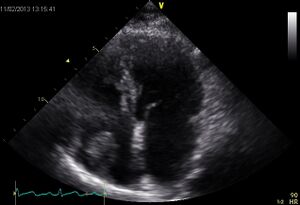
|
| Myxoma LA
|
Thrombus RA
|
| Video
|
|
| Vegetation TV
|
|
References
<biblio>
- 1 Hamer, J.P.M. “Cardiale massa’s”, in: Hamer/Pieper, ‘Praktische echocardiografie’, (2006), 1e druk 2e oplage, Houten, Bohn Stafleu van loghum, p.198-207.
</biblio>
