Pulmonary Artery: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|bgcolor="#FFFFFF"|[[Image:Pulmart.png|200px]] | |bgcolor="#FFFFFF"|[[Image:Pulmart.png|200px]] | ||
Picture Source: Cove Point Foundation<cite>1</cite> | |||
|} | |} | ||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" width="800px" | {| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" width="800px" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="5"|'''PA diameter''' | |colspan="5"|'''PA diameter'''<cite>2</cite> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 45: | Line 47: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
#1 | #1 [http://www.pted.org/?id=pulmhypertension1 Cove Point Foundation - Congenital Heart Disease] | ||
#2 pmid=3730205 | #2 pmid=3730205 | ||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
Revision as of 07:57, 7 January 2014
Anatomy
The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. It is the only artery that carries deoxygenated blood transported.
The pulmonary trunk (TP) starts from the pulmonary valve is ± 5 cm and ± 2 cm in diameter. Then splits into two branches, the trunk, the left-hand (aps) -, and right pulmonary artery (APD), which carry the oxygen-depleted blood to the corresponding lungs.
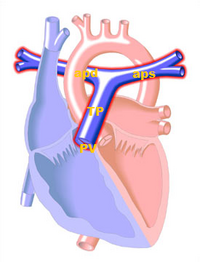
Picture Source: Cove Point Foundation[1] |
| PA diameter[2] | ||||
| Reference range | Mildly abnormal | Moderately abnormal | Severely abnormal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1cm Below pulmonic valve | 1.5–2.1 | 2.2–2.5 | 2.6–2.9 | ≥3.0 |
|
|
| Plax by tilted (Plax PV) | PSax Ao |
|---|---|
|
|
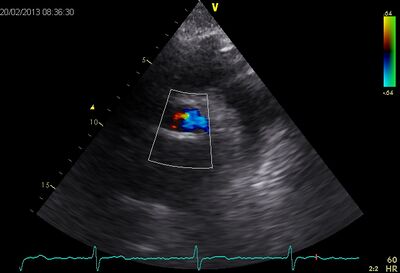
| Suprasternal apd (color doppler) | Dilated apd (Plax PV) |